Using Milkomeda's Asset Consolidation Contracts (MACC)
Note: If you are already familiar with Milkomeda Assets Consolidation Contracts, you can skip ahead to the step-by-step guide to learn how to interact with the MACC DApp.
Context
Bridges are an essential part of the Milkomeda ecosystem, as they allow users to move different assets from Cardano to Milkomeda C1 so they can enjoy the benefits of the interoperability solutions. However, the existence of multiple bridges to bridge the same assets, results in the fragmentation of assets since each bridge will have its own version of the wrapped asset.
Taking USDC as an example, the Celer Bridge will wrap the asset as ceUSDC while Multichain will wrap the asset as multiUSDC, although both tokens represent the same asset.
This creates two perfectly identified but undesirable issues, which are liquidity fragmentation of each bridged asset and poor user experience, especially for new users who are less knowledgeable about the reason and meaning of the different variants of the wrapped tokens.
On the issue of liquidity fragmentation, this can refer to fragmentation across different DEXes, which is not necessarily undesirable nor avoidable, but more importantly, it can also refer to the fragmentation of liquidity between the different wrapped alternatives of the same asset.
When a popular stablecoin, like USDC, is fragmented into multiple issued fragmented assets, the liquidity is also fragmented. This means that a user swapping ceUSDC/mADA on any given pool will experience higher slippage compared to the case if the liquidity was concentrated in a single pool of USDC/mADA.
For instance, if a user wants to swap mADA for USDC on any popular Milkomeda DEX, they will be presented with multiple versions of USDC to choose from, which can be confusing. This is not an issue with the UI&UX of that particular DEX, but rather a result of fragmented liquidity.
Another concern with blockchain bridges is the possibility of hacks. Users who hold wrapped assets on a certain bridge are exposed to that particular bridge, and choosing one bridge over another can turn out to be a bad decision in case of a hack. But what if users could be indifferent to the bridge they choose when bridging their assets?
Milkomeda Assets Consolidation Contracts (MACC)
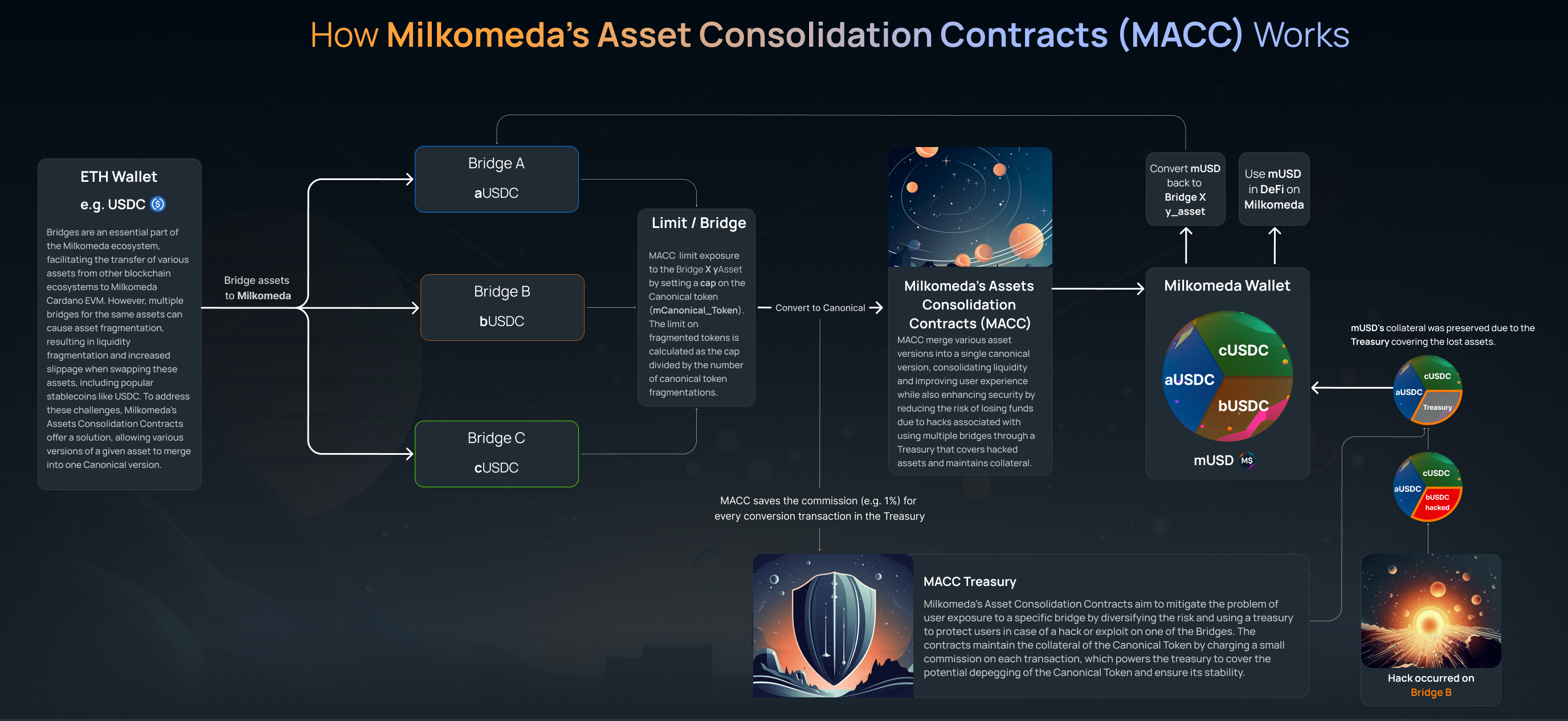
The aforementioned issues could be addressed by implementing a proposed solution called Milkomeda Assets Consolidation Contracts. These smart contracts enable merging different versions of a particular asset into a single canonical version. This would effectively consolidate the fragmented liquidity of a stablecoin like USDC, which can improve user experience and potentially mitigate the consequences of hacks associated with using multiple bridges. Canonical Smart Contracts for token merger are essentially two contracts:
- TokenMerger implemented through an ERC1967Proxy and is ownable,
- CanonicalToken, an ERC20 that serves as the canonical version of fragmented ERC20 and that can only be minted by the TokenMerger contract (the proxy).
To put it simply, the TokenMerger serves as a conversion contract between the various versions of a particular asset, referred to as Fragmented Tokens, and the Canonical version of the same asset. The TokenMerger is equipped with a whitelist for each Fragmented Token asset, which specifies the allowed assets that can be converted.
Through the use of Milkomeda Canonical Smart Contracts, it would be possible to consolidate the various versions of a particular asset into a single canonical version. This consolidation would address the issue of liquidity fragmentation among different tokens, resulting in a better user experience. Essentially, a single version of the asset would be used, solving the problem of fragmented liquidity and the poor user experience associated with it.
Suppose we establish a Asset Consolidation Contracts for mUSDC (Canonical asset). User A transfers 10ceUSDC to this contract and receives 10 mUSDC in exchange. Next, user B sends 20multiUSDC to the smart contract and receives 20mUSDC in return. Previously, users A and B would have been required to deposit their funds in separate liquidity pools, such as ceUSDC/mADA and multiUSDC/mADA. However, by canonizing their assets into mUSDC, they can now combine their liquidity in the same pool, mUSDC/mADA.
Treasury
The Milkomeda Assets Consolidation Contracts aim to mitigate the problem of user exposure to a specific bridge by diversifying the risk. The risk diversification is achieved by having each Canonical version of an asset backed by multiple bridges. In case of a hack or exploit on an individual bridge resulting in the depegging of a corresponding Fragmented Asset, MACC will pause the conversion to Canonical asset from that specific token to prevent further losses for users and to avoid off-ramping hacked assets. To protect users who converted their assets to the Canonical Token before a hack, our treasury will cover the potential depegging of the Canonical Token.
Following infographics aims to show how MACC and Treasury works:
Users can convert back to any Fragmented asset (e.g. ceUSDC) on a daily basis, provided that the specific token has achieved sufficient liquidity and has not been impacted by a hack on its corresponding bridge.
The amount of assets that can be converted to MACC from each bridge depends on the amount of assets in the treasury at each time. For instance, if there are three bridges, the maximum amount of assets that can be converted from each bridge will be determined by the Treasury cap.
If one of the bridges is hacked and suffers losses (up to one-third of the collateral), the treasury must have enough money to cover those losses completely.
The smart contracts have a limit on the amount of Fragmented tokens that can be converted to Canonical representation, which ensures that the exposure to any one Fragmented token is limited. This limit is determined by setting a cap on the amount of Canonical tokens.
Milkomeda Assets Consolidation Contracts limits the exposure to the fragmented token by setting a cap on the canonical token. The limit of fragmented token is then cap / (# of canonical token fragmentations).
In addition, each conversion made through MACC incurs a small commission, which is collected and deposited into the Treasury. In the event of a hack on one of the whitelisted bridges, these funds are used to cover the value of the affected assets, helping to maintain the price of the canonical asset and preserving user trust.
List of supported Fragmented tokens in MACC:
| Token name | Token Ticker | Contract Address Details | Token Type | Canonical Token Representation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ceUSDC | ceUSDC | 0x6a2d262D56735DbA19Dd70682B39F6bE9a931D98 | ERC-20 | mUSDC |
| multiUSDC | multiUSDC | 0xB44a9B6905aF7c801311e8F4E76932ee959c663C | ERC-20 | mUSDC |
List of MACC Canonical tokens:
| Token name | Token Ticker | Contract Address Details | Token Type | Fragmented Tokens Allowed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mUSDC | mUSDC | 0x063139a927FE02B3a6A5E0d5B48c8BeDFA7de954 | ERC-20 | ceUSDC, multiUSDC |
A Comprehensive Step-by-Step Guide to the MACC DApp
To begin using the MACC DApp, you will need an asset that is supported by the platform (currently only bridged USDC), as well as some mADA to cover the network transaction fee. To interact with MACC DApp you can use Metamask, Flint, NuFi or Wallet Connect.
The following article presents a step-by-step guide for using MACC DApp on Milkomeda C1 devnet, where TKNA (devnet representation of ceUSDC) and TKNB (devnet representation of multiUSDC) represent the fragmented assets that are accepted by the whitelisted bridges, while MRGER is a Canonical Representation (on mainnet - mUSDC).
Step 1 : Connect your Wallet
To get started with the MACC DApp, go to the MACC homepage.
Once you arrive there, you'll need to connect your wallet to proceed. To do this, you have two options. You can either click the "Connect Wallet" button located in the top right corner of the connect page, or you can go directly to the converting page.
The hero section of the MACC now includes a data section that provides valuable information at a glance. This section allows you to quickly check which bridgers are currently supported by the MACC, as well as the number of assets that have been converted from each of them. In addition, you can easily review the available liquidity and cap for the Canonical Token, as well as the balance of the Treasury.

Please be aware that in order to connect to the MACC DApp, you must use one of our currently supported wallets, such as Metamask, Wallet Connect, or Flint. Once you have selected your preferred wallet, you can proceed to the convert page and begin converting your assets.

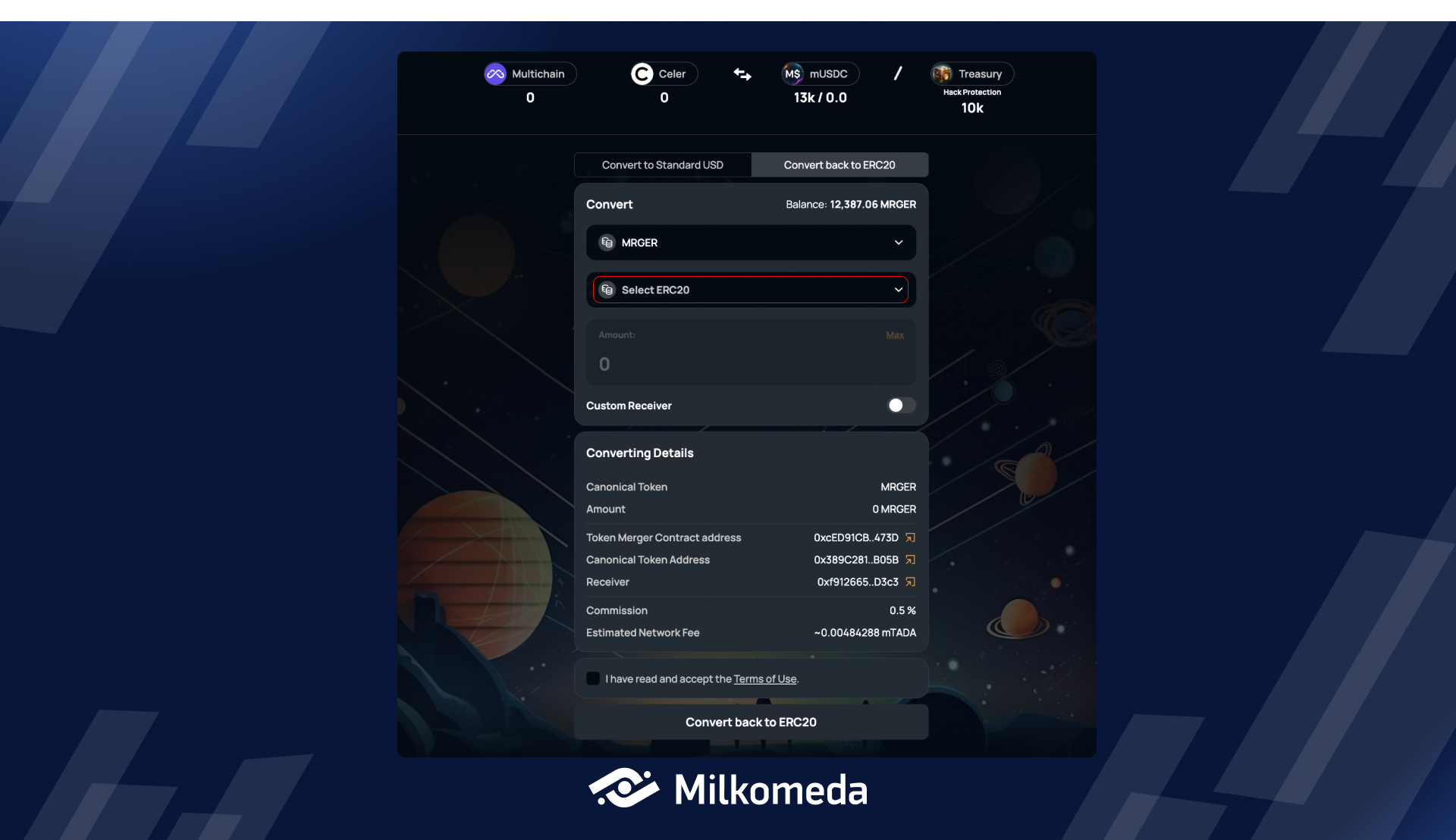
Step 2 : Select the Fragmented asset you wish to convert
To start converting your Fragmented asset use the Select ERC-20 drop-down and choose the asset you want to convert.
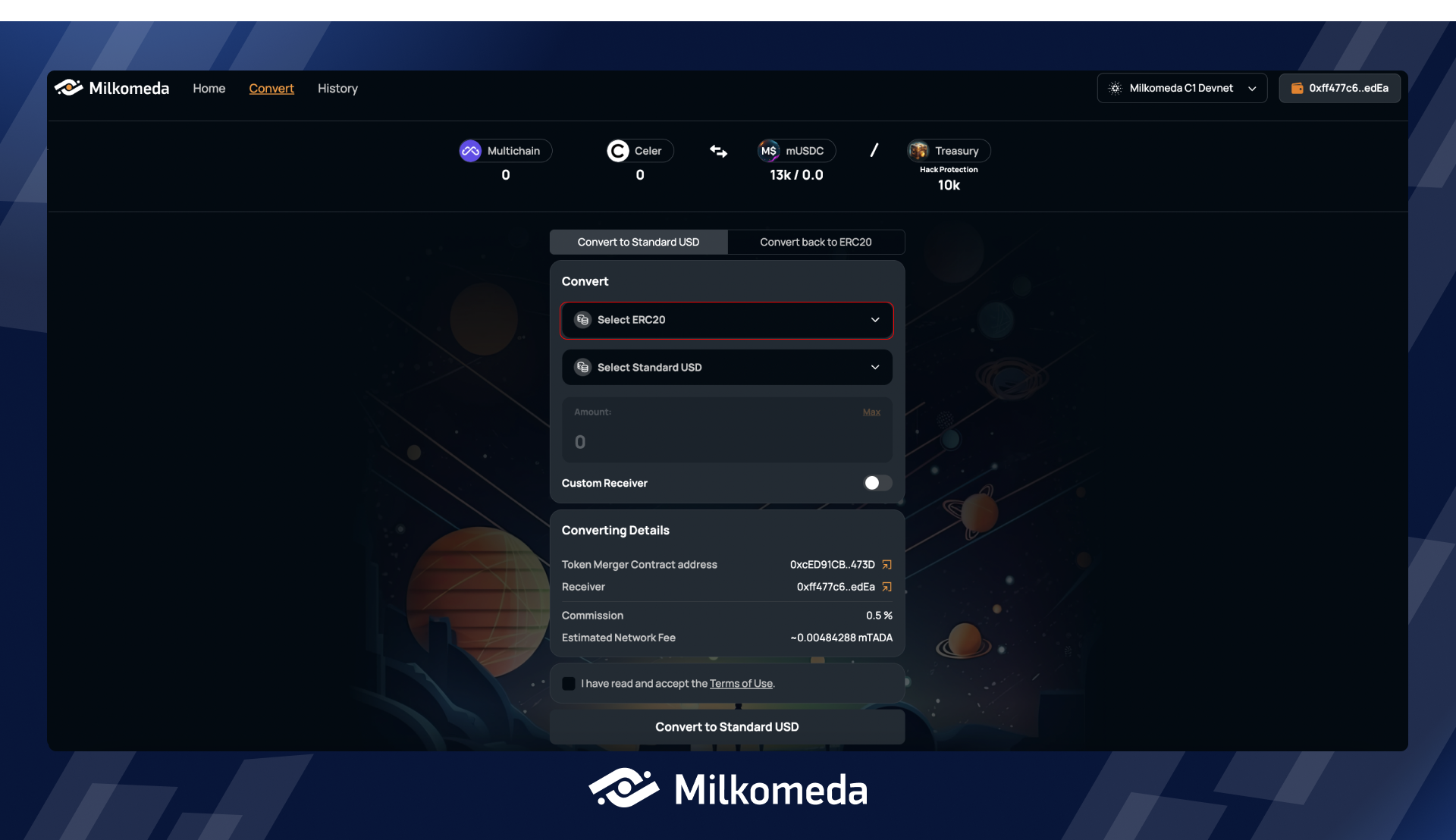 To begin the conversion process, select the asset you wish to convert from the drop-down menu. For the purpose of this tutorial, we will be converting TKNA, which represents one of the fragmented assets of Bridge A.
To begin the conversion process, select the asset you wish to convert from the drop-down menu. For the purpose of this tutorial, we will be converting TKNA, which represents one of the fragmented assets of Bridge A.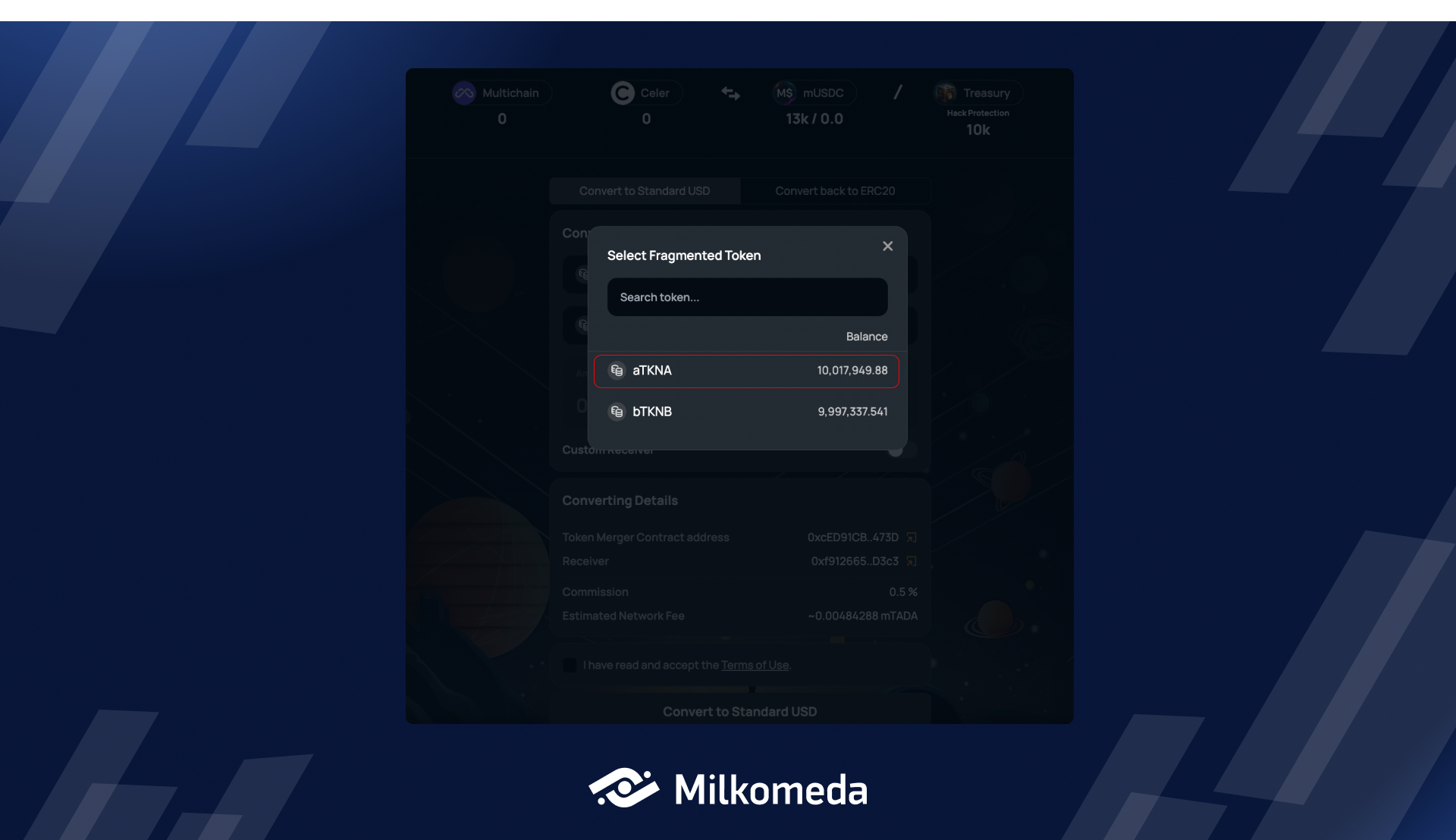
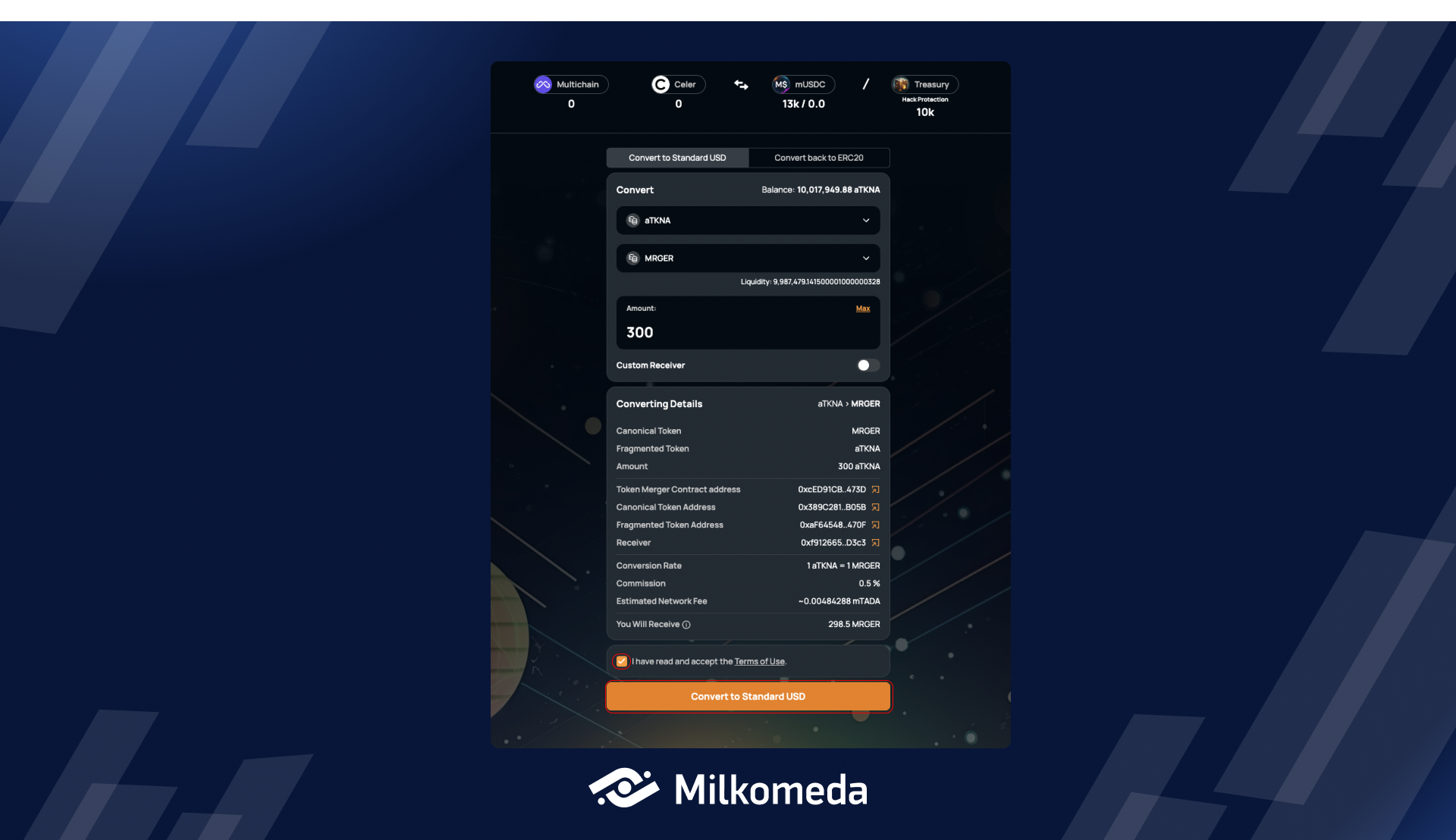
Once you have selected the fragmented asset and entered the amount you wish to convert, the MACC DApp's user interface will calculate the amount of Canonical Token you will receive in return. As shown on the following screen, the Canonical Token (pre-populated as MRGER token) will be displayed after you have entered the required amount to be converted.
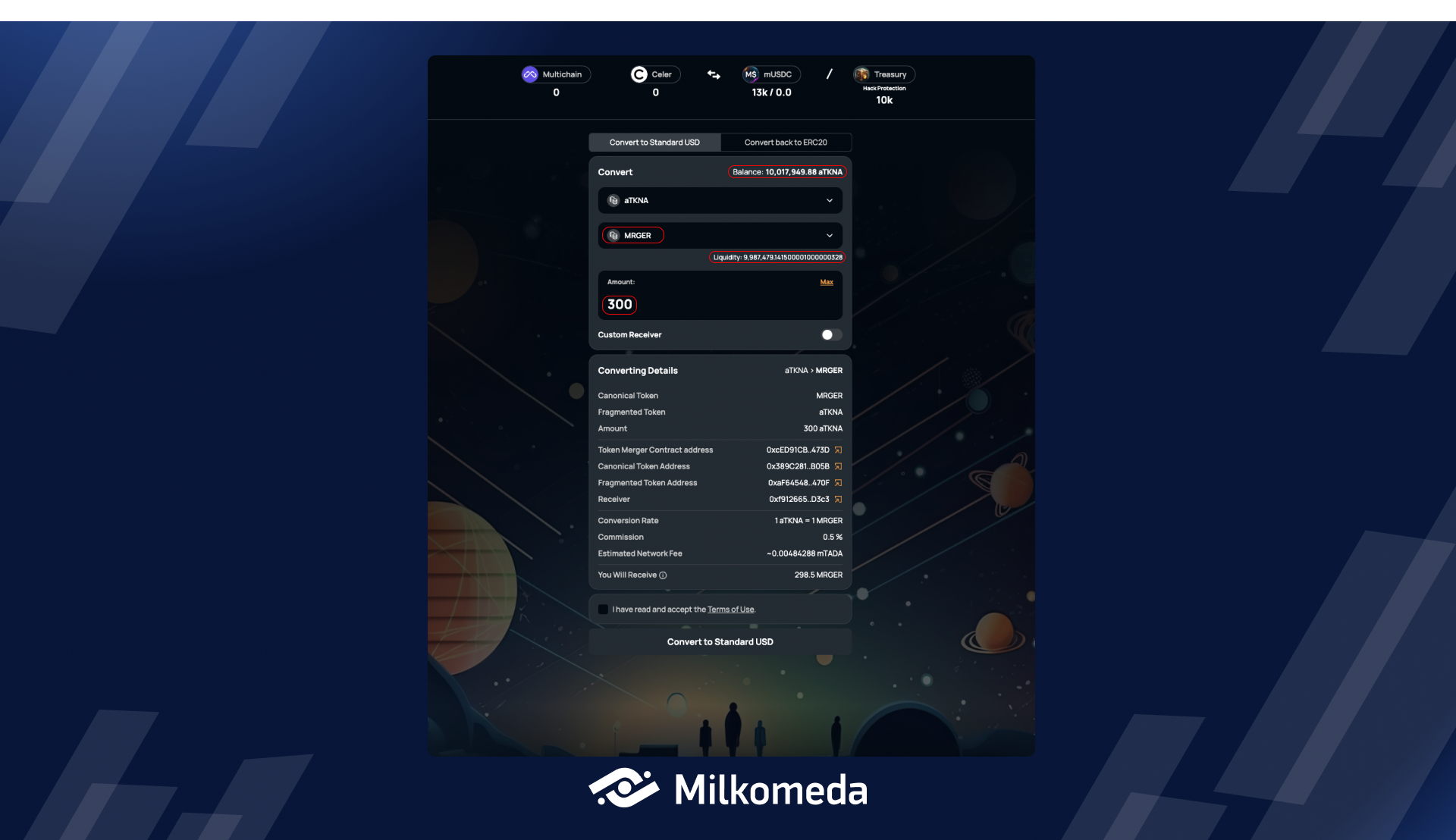
On the mainnet deployment, you should see mUSDC, which represents the Canonical token of USDC-fragmented assets.
Once you enter the desired amount for conversion, the UI will display supplementary information.
- The top corner of the "Convert to Standard USD" tab conveniently displays your wallet's balance for the chosen fragmented asset.
- Below the chosen Canonical Token, you will see its available liquidity. If the amount you enter exceeds the available liquidity, you will receive a message informing you of this fact.
- You can also choose a custom receiver.
- The DApp UI will display converting details such as the assets you are converting, the typed amount, contract addresses, conversion rate, commission percentage, and estimated network fee.
Before proceeding with the conversion, please double-check all the information displayed on the DApp UI and make sure you are familiar with the Terms of Use. In the next step, you will need to accept the ToU to be able to convert your fragmented assets.
Step 3 : Convert your Fragmented Assets
To initiate the conversion process, you will need to accept two transactions. The first transaction permits the DApp to access the tokens in your wallet, and once the network confirms this transaction, you will be prompted to accept the conversion transaction. This two-step process is standard to ensure that no DApp can empty a connected wallet without the user's approval.
3.1. Set a spending cap for your Fragmented asset

3.2 Confirm the conversion transaction in your Metamask wallet.

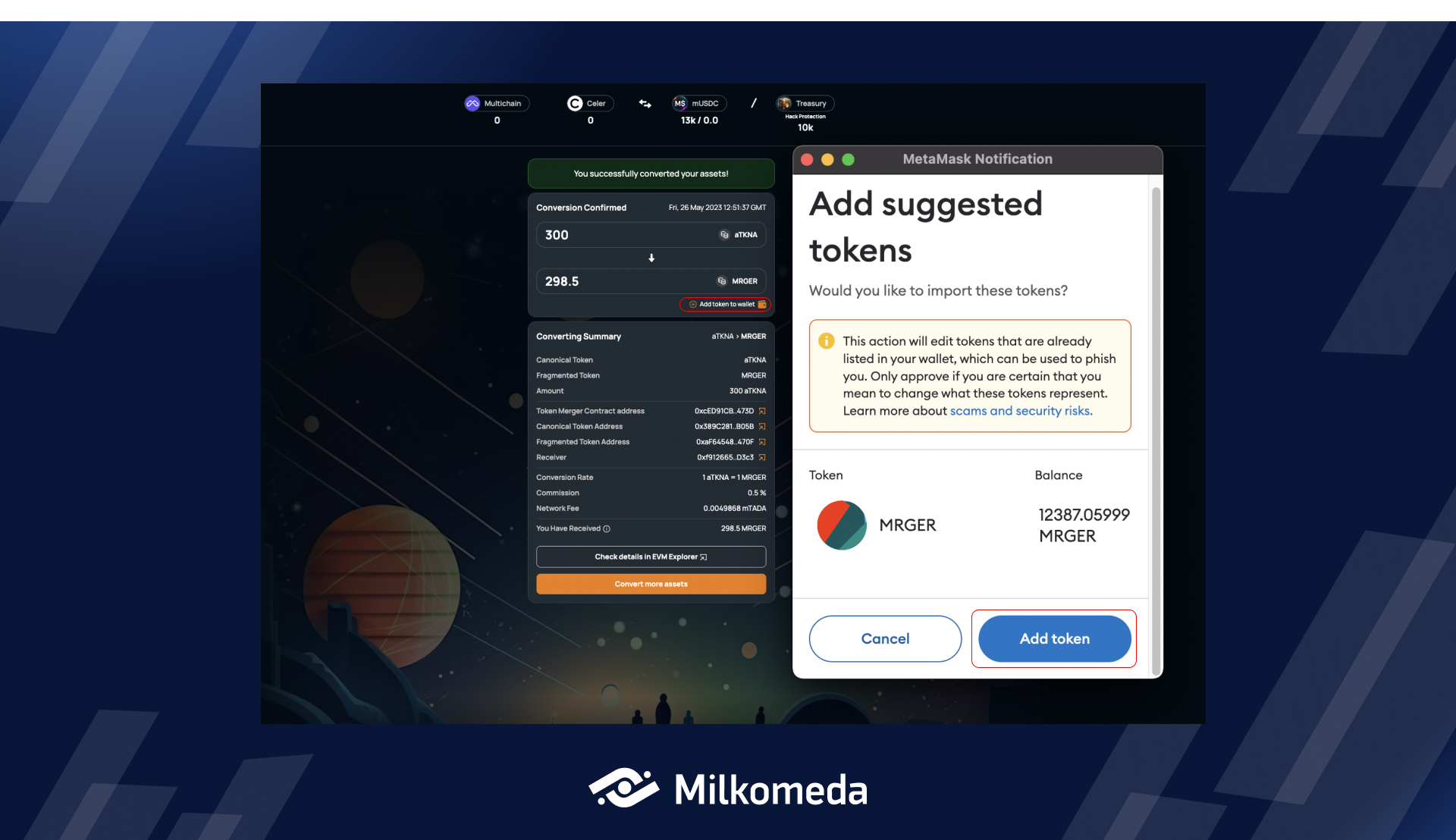
Success! You converted your Fragmented assets
After the conversion transaction has been confirmed on the network, you can view the summary of your conversion. As a final step, and this only needs to be done the first time you convert to a particular canonical asset, you need to add the canonical asset to your wallet. To add the Canonical Token to your MetaMask wallet, simply click + Add token to wallet. MetaMask will prompt you to add a custom token to your wallet, and you'll be able to view its balance immediately.
MACC DApp Transaction History
Once you have completed your first successful conversion, you can easily track it by visiting the MACC Transaction History Tab. To access this page, simply click on the "Transaction History" from the main navbar or click this link, you will be able to view all Milkomeda's Assets Consolidation Contracts transactions.

Converting Canonical assets back Fragmented version
To convert canonical assets back into a fragmented asset, follow a similar process as mentioned above, with the only difference being that you can convert to a different fragmented asset than the one you originally converted from.
Step 1: To begin, select the "Convert back to ERC20" tab on the MACC DApp.
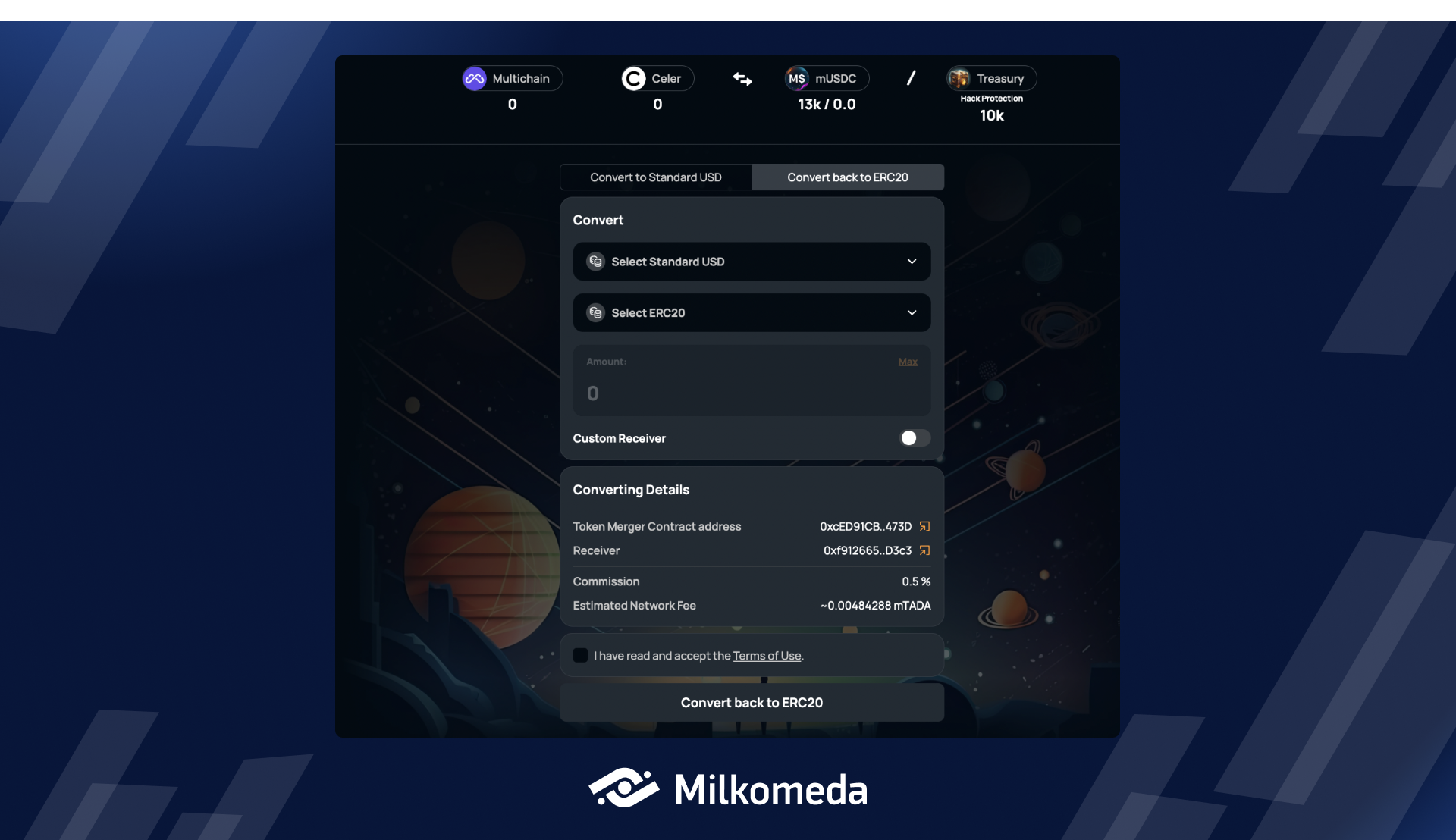
Step 2: Select Canonical asset
To begin, choose the canonical asset that you want to convert from the token selector located at the top. For the purposes of this tutorial, we will be using the MRGER token (canonical asset) that was received earlier. It is important to note that the MACC DApp will support multiple canonical assets in the future.
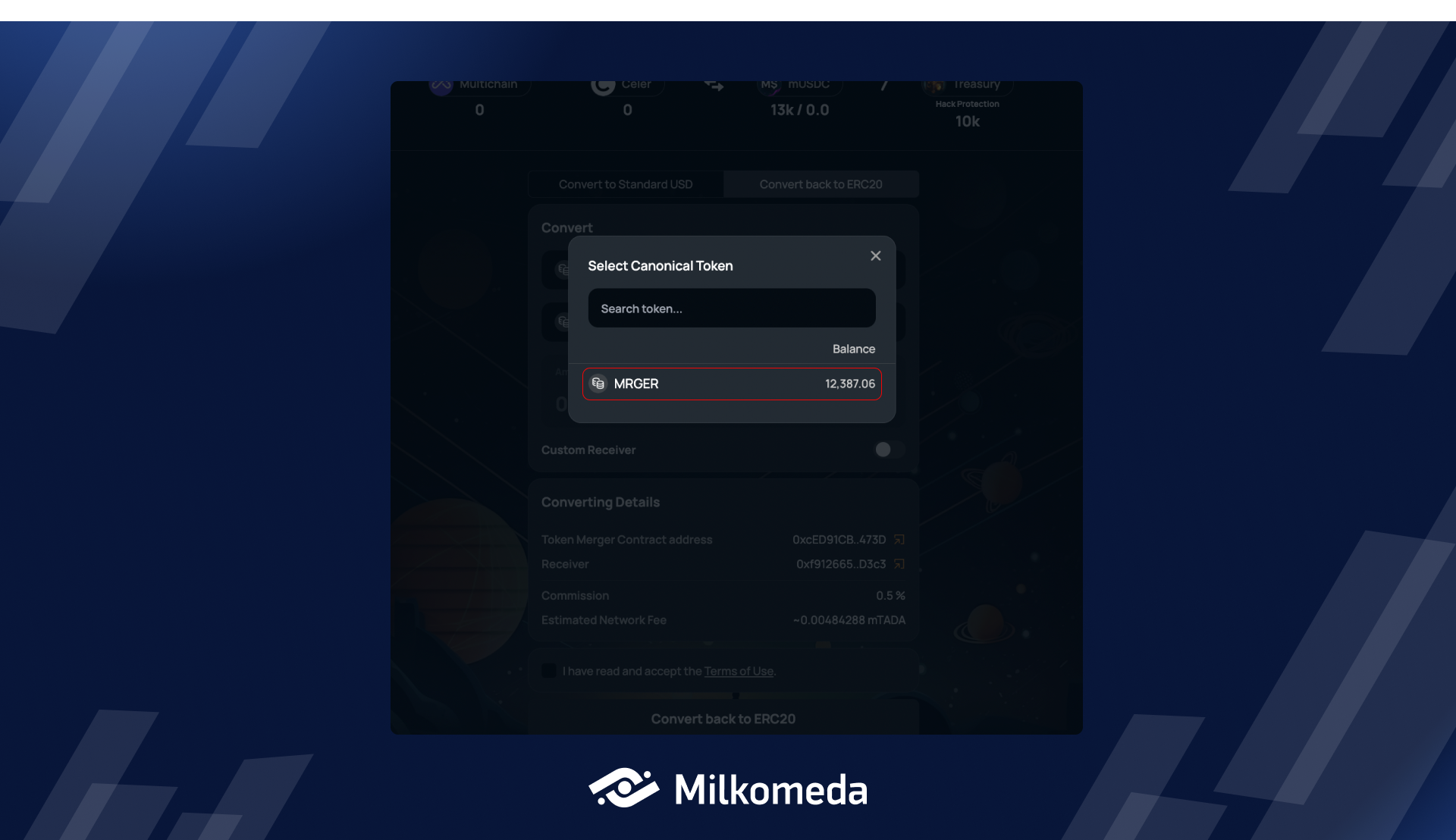
Step 3: Select Fragmented asset
Now you need to select which Fragmented asset you want to convert your Canonical asset back to.
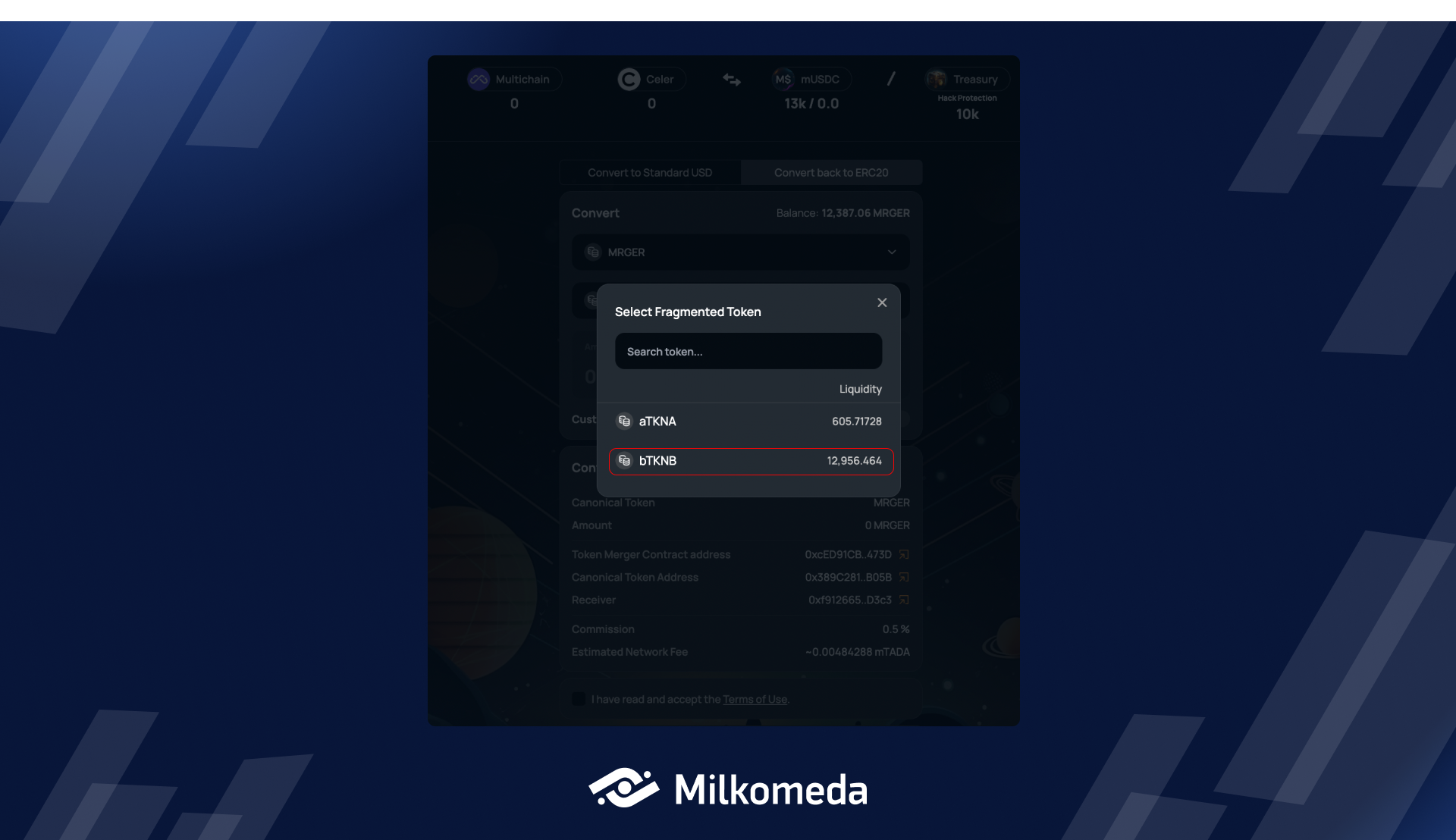
When you open the Fragmented token drop-down, you'll see a list of supported Fragmented assets that you can convert your Canonical asset back to.
However, please keep in mind the following rules:
- The Fragmented token must have sufficient liquidity for the conversion to occur.
- The Fragmented token must not have been compromised by any hacking or exploitation attempts.
Example: If you aim to convert 300 MRGER to Token A, but the current available liquidity for Token A is lower than the desired conversion amount, you will only be able to convert up to the maximum liquidity available. In case you try to convert more than the available liquidity, the DApp UI will display a warning message to alert you.
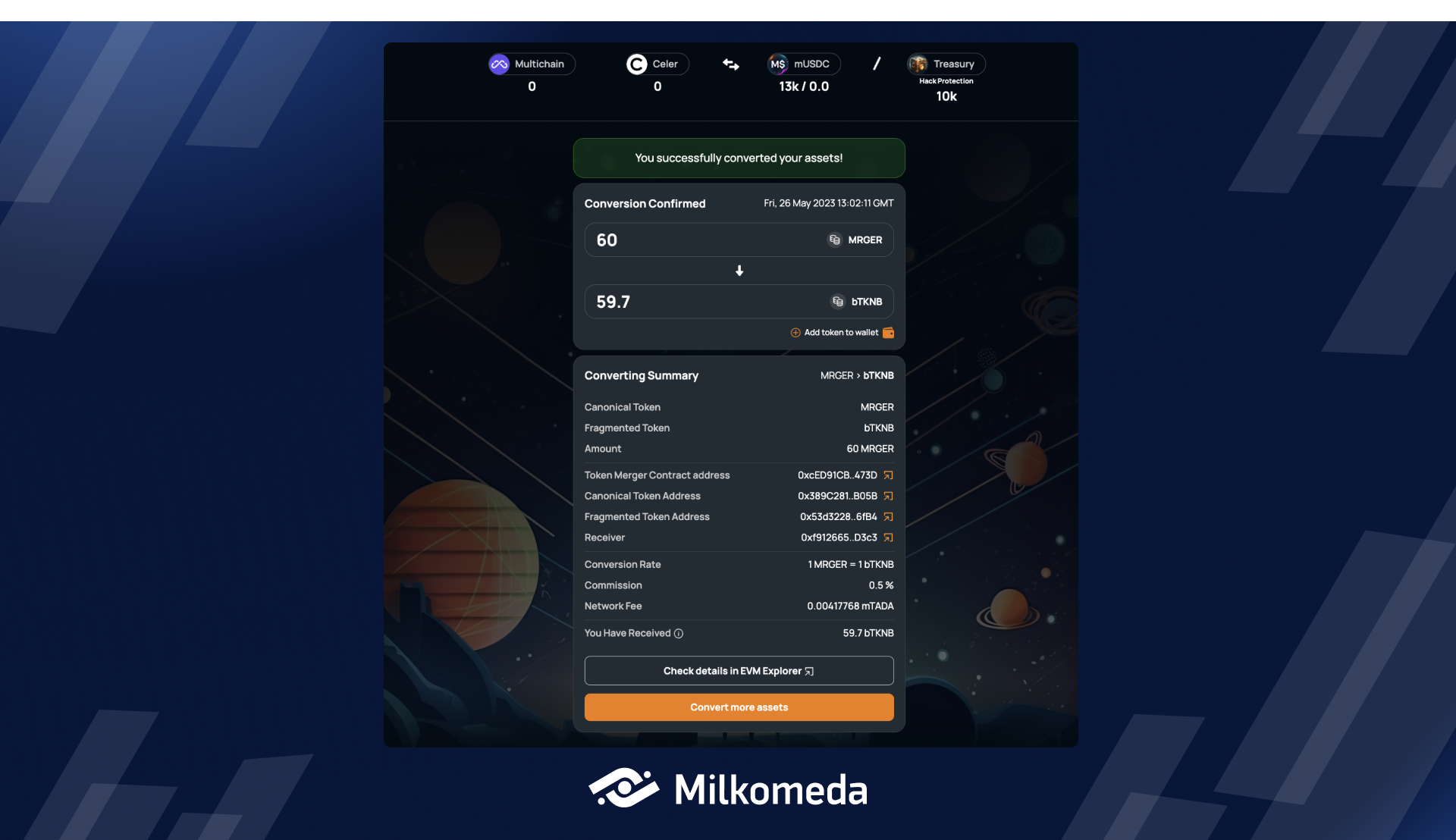
To convert your Canonical asset back to Fragmented tokens, follow the same process as converting Fragmented tokens to their Canonical representation.
In this example, we will convert 60 MRGER tokens back to Token A.
After the network has processed your transaction, you have successfully converted your Canonical asset back to a Fragmented token. If this is the first time you have held this Fragmented token in your wallet, you can add it to your MetaMask by clicking the Add token to wallet button.
Once you have completed your conversion, you can easily track it by visiting the MACC Transaction History Tab. To access this page, simply click on the "Transaction History" from the main navbar or click this link, you will be able to view all Milkomeda's Assets Consolidation Contracts transactions.
Summary:
Canonical smart contracts and the MACC DApp solve the persistent problem of fractionalized assets and improve the DeFi experience on Milkomeda for all involved while help protect your assets from potential bridge exploits! This guide provides step-by-step instructions for converting fragmented tokens to their canonical representation and back, using the Milkomeda's Assets Canonicalization Contract (MACC) DApp.