Introduction
Staking on Cardano
Staking is an integral part of the Cardano blockchain's consensus mechanism and incentivization system. This fundamental process empowers Cardano holders to actively engage with the network and be rewarded with additional ADA for their participation. Notably, staking plays a crucial role in maintaining the network's decentralization and overall security.
Cardano stands out as a leading network with one of the highest staking participation rates, surpassing even well-established projects like Ethereum, with close to three-quarters of the native token (ADA) staked.
When users stake their ADA, they cast a vote for a validator and join a pool alongside hundreds or thousands of other stakers. This process, known as delegating, enables ADA holders to delegate their assets to a specific pool, thereby increasing the pool's staked ADA. Higher staked pools have a greater likelihood of being selected to build blocks and earn rewards.
Liquid Staking
On some chains, like Ethereum, staking one's asset results in that asset being locked and cannot be used while it's staked, i.e., it's iliquid. Liquid staking normally refers to a process that allows users to stake their cryptocurrencies, typically on proof-of-stake (PoS) networks, while receiving a liquid representation of their staked assets in return.
When a user stakes on Cardano, his ADA remains in his wallet and it will have to remain there for a particular epoch to receive rewards, so when he moves his funds to a Layer 2, they will no longer be in his Layer 1 and no rewards will be received.
In contemplating Layer 2 adoption, users often weigh the advantages and disadvantages of transitioning from Layer 1, because while Layer 2 offers improved scalability in terms of speed and cost, there may be some trade-offs in terms of security compared to Layer 1.
However, since many blockchains, and Cardano in particular, offer rewards to users for participating in staking and governance on Layer 1, it becomes crucial to ensure that users continue to earn these rewards even after moving their funds to Sidechain networks.
Milkomeda Liquid Staking
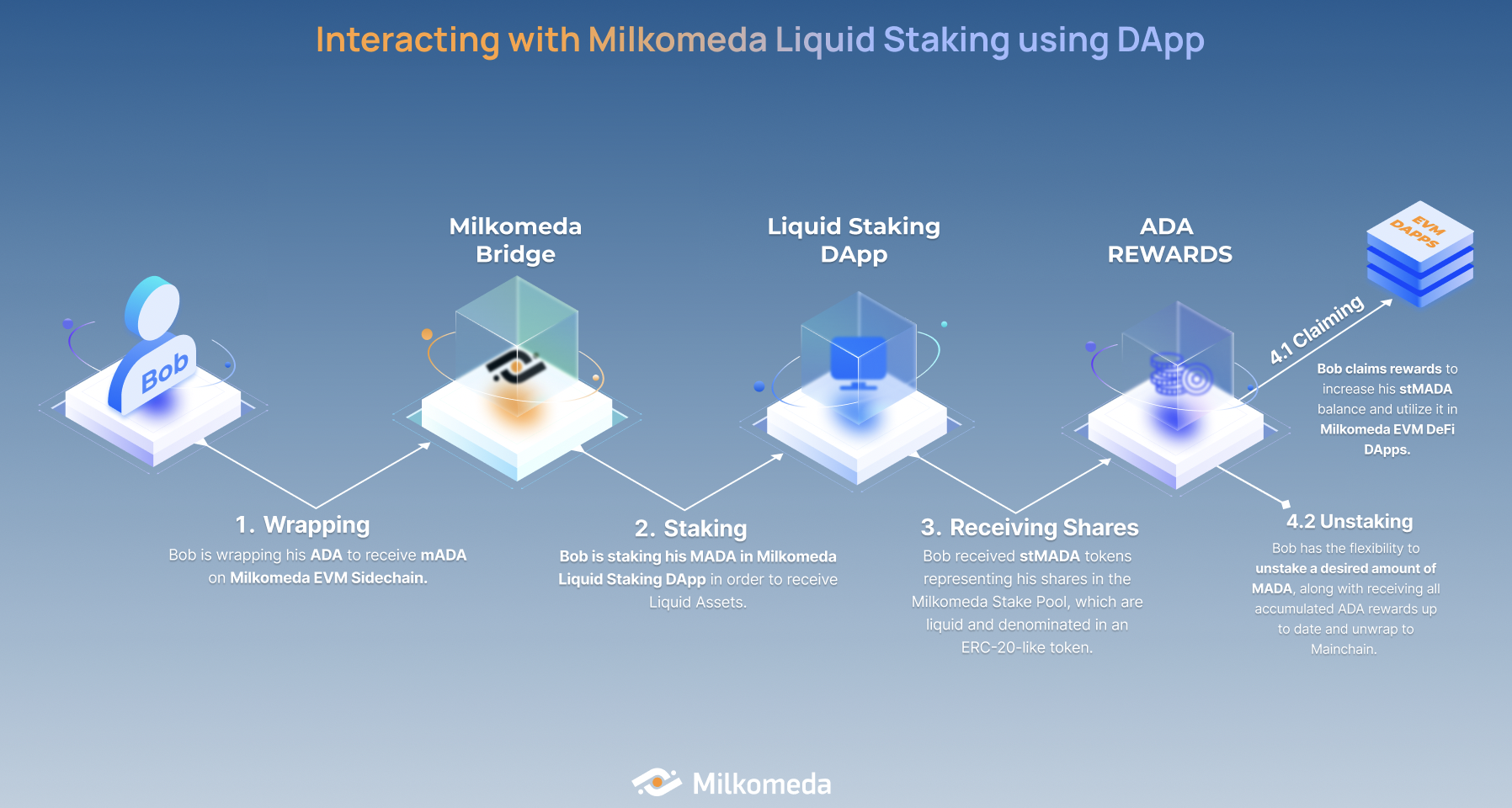
To enable a seamless continuity of rewards, Milkomeda has developed a Liquid Staking standard that enables users to participate in a staking protocol while retaining custody of their funds. Users receive a yield-bearing tokenized representation of their staked assets, ensuring they continue to earn rewards effortlessly.
In the case of Cardano, users can stake their mADA (a wrapped representation of ADA) to receive stMADA, which accrues Layer 1 staking rewards.
By implementing Liquid Staking and enabling rewards accumulation on Layer 2 solutions, blockchain platforms like Cardano aim to create an ecosystem that incentivizes user engagement, fosters developer innovation, and generates sustainable protocol revenue across multiple layers of the network. This approach ensures the network's continued growth and success while rewarding active participants.
For a comprehensive understanding of the process, we recommend you read our Liquid Staking Documentation.